HTML Forms
What Are HTML Forms?
Forms are an HTML component used to get user input. An HTML form will look like this:
<form action="" method="POST">
<!-- data input components here -->
<input type=submit>
</form>
Notice that HTML forms will consist of three main components:
- The action: Which determins to which URL the data will be sent, we typically keep this empty to send the data to the same view in Django
- The method: Which determins how the data will be sent and can be either POST or GET
- The input components: Which determine what input is needed from the user. Remember we must always include the
submittype input.
Data Input Components
Depending on what type of information we need from the user, we can include different input types inside the form and the browser will display the appropriate GUI compoenent. We also use labeltags to set the label for each input component.
For example, to get the username and password from the user, we include the following tags inside the form tag:
<form action="" method="GET">
<label for="username">Username:</label>
<input type="text" name="username">
<label for="pwd">Password:</label>
<input type="password" name="pwd">
</form>
Notice how these tags are place inside the form tag, which means that the information needs to be sent to the url specified in the action using the method specified in the method attribute of the form.
input tag is the name attribute. We can chose whatever name we want, we just need to make sure it is unique. When the data is submitted, it will be placed in a variable with the same name included in the name attribute.The form would look something like this in the browser:
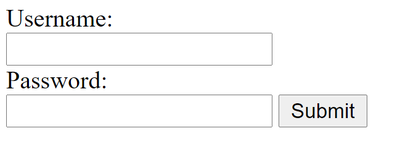
Other input types include:
- password
- radio
- checkbox
- button
- and many more that can be found here
Handling Form Input in Views
The data from the form will be included in the request variable in the view that the form was submitted to. If the form type is GET then the data will be in the dictionary request.GET. If the form method was POST, then the data will be in the dictionary request.POST.
Both request.GET and request.POST are python dictionaries and everything you know about dictionaries applies here. You can fetch the data using a key that matches the name attribute from the input. In our previous example where we had a text input named username and a password input named pwd we would fetch the data inside them using:
# For GET form method
request.GET['username'] # for username
request.GET['pwd'] # for password
# For POST form method
request.POST['username'] # for username
request.POST['pwd'] # for password
You can use the dictionary values as if you would use any variable in Python. You can also use the dictionary get method instead of using the indexing opertor [].
GET Vs POST
Anything you can do with GET you can do with POST forms. The only difference is that the data in POST forms is sent within the HTML request body, whereas the data for the GET method will be sent through the URL where the user can see the data.
The preferable method of course is POST as it makes the URL less cluttered and provided the communication is encrypted using HTML and we start using the Django Form features, will be more secure as the data cannot be read by anyone from the url.
So use GET in cases where the data is not critical and you need the convenience of changing the data easily from the URL. For example, in search queries and simple data submission, never for username and passwords. Otherwise, use the POST method.
Final Thoughts
- Using forms the way we did is not secure
- You can use it for search queries and simple input
- Django Forms is used to make forms more secure
- Covered in future topic
Review Questions and Challenges
- What is the difference between POST and GET form methods?
- What does the action attribute of the form do?
- Name 3 different input types for html forms.
- What input type would you use to make the user choose one option from 3 (e.g., choosing their major from many)?
- What input type would you use to allow the user to choose multiple options from many (e.g., choosing topigs for a pizza)?
- Create a calculator view where the user:
- Inputs two values
- Chooses the operation
- Gets the result when the form is submitted
- Create a Fehrenhite to Celsious converter where the user would input the degrees in Fehrenheit and the application would output the degrees in celsious. The application should also allow the user to convert the degree the other way around. Here are the formulas:
- C to F: $C * 9/5+32 = F$
- F to C: $(F - 32) * 5/9 = C$
- You can implement the application in a single or multiple views