ISOM 350
Business Application Development
Mohammad AlMarzouq
Django View Functions
Reminder of Django’s MVT Model
Main components in a Django web application are:
- Models: To handle data
- Views: To handle business logic
- Templates: To handle how screens will look
This organization enables team collaboration and specialization
Django Application Views
- A view refers to the webpage in a web application that implements a functionality
- For example, login, cart, payment, catalog, and blog list screens.
- A view function is that function that is used to constructs the view in response to the browser requesting it
- It brings together the data performs the actions necessary to construct the page to be sne to the browser
Building A View
The required tasks to build a view are:
- Create the view function in your app’s views.py
- Link the view function to a path in root urls.py
- (Optional) Prepare the template that has the design of the page
Data handling is done as part of creating the view function.
View Functions
- Receive HTTP requests
- Perform a task
- Then return an HTTP response
Understanding The View Function
In your app views.py:
def test_view(request):
print(f"Request: {request}")
Continue With test_view
Now link the view function to a url path:
Update mysite/urls.py:
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from blog.views import test_view
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('test/', test_view),
]
Test The New View
- Run the Django development server and you will notice:
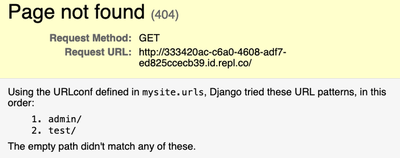
What is Django Telling you?
- 404 is a standard HTTP response code, it means that page you requested does not exist
- Which page is that?
- The available paths are
/admin/and/test/- Where were they defined?
- how can we fix the 404? do we need to?
- How do we run our test_view?
Continue Test The New View
- Point your browser to the path /test
- You need to pay attention to the output in two places:
- The browser
- The console (on replit.com)
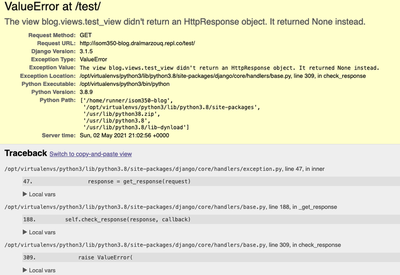
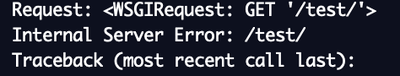
Continue Test The New View
- Can you explain what just happened?
- How can we fix the ValueError?
Solution
If your response was:
Let test_view return an HTTP Response
Then you are correct!
Fixing test_view
from django.http import HttpResponse
def test_view(request):
return HttpResponse("Hello World!")
But What About HTML?
- Browsers are capable of rendering HTML
- Include HTML in the HttpResponse
from django.http import HttpResponse
def test_view(request):
return HttpResponse("""<html><body>
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
<p>This is my first <strong>html</strong> web app!</p>
</body></html>""")
FStrings Can Make HTML Dynamic
from django.http import HttpResponse
def test_view(request):
name = "ISOM 350 Student"
return HttpResponse(f"""<html><body>
<h1>Hello {name}!</h1>
<p>This is my first <strong>html</strong> web app!</p>
</body></html>""")
User input will be a future topic
See forms
Of course, we will not be writing HTML using Python Strings.
This is where Django Templates are most useful
Summary
To create a fully functional web page in Django you need:
- Create a view function to service this page
- Create a path for the function in urls.py
- Prepare the template for the page
Models will be used only if databases are needed and will be accessed from the view function.